
Pain in the joints- These are unpleasant pains, pulling sensations in the area of the joints, the intensity of which sometimes reaches the level of pain. The symptom is combined with muscle pain, weakness, weakness, crunch, limited movements and may precede joint pain (arthralgia). Joint pain is accompanied by lesions of the musculoskeletal system, infections, diseases of the hematopoietic system and vascular pathology. To determine the cause of the disorder, laboratory tests, ultrasound, radiography and invasive methods are used. Treatment includes treating the disease that caused the pain.
Causes of joint pain
Mild or moderate discomfort in the joints is not always a manifestation of a pathological process. Sometimes the symptom has natural causes. Transient pains in the joints are felt when wearing uncomfortable shoes, and in weather-sensitive people - when the weather changes. During puberty, pain in the shoulder and knee joints is caused by insufficient blood supply due to accelerated bone growth.
Significant physical activity
During intense training or hard work, the common cause of the symptom is overstrain of the musculo-ligamentous apparatus, less often it is caused by microtraumas of the cartilage and synovium. A typical combination of joint pain and bone and muscle discomfort. Discomfort in the joints and muscles appears immediately after impact physical activity or against the background of prolonged monotonous work with constant tension in the same muscle groups. Pain in the joints of the body occurs without fever. With large overloads, a moderate disturbance of the general condition and weakness is possible.
The disorder can last up to several days and with limited physical activity it gradually decreases until it disappears completely without any treatment. If pain as a result of sports or heavy physical work is replaced by constant pain, swelling of the wrist, elbow, shoulder, ankle, knee and hip joint and limitation of usual movements, you should see a doctor.
Age-related changes in the musculoskeletal system
The causes of moderate bone and joint pain in the elderly are degenerative processes with calcium loss, thinning of the bone beams, impaired blood supply to the cartilage and a decrease in the volume of intra-articular fluid. Mild discomfort is only the first manifestation of senile joint damage. Usually, periodic discomfort appears after 45-50 years. By the age of 60-65, unpleasant pain appears even with minor effort, accompanied by stiffness of movements, stooping, shifting gait and gradually gives way to pain.
Pregnancy
Complaints of joint pain are more common in the second half of the gestational age. Pulling, painful discomfort is usually felt in the joints of the pelvis and lower limbs. Intensifies towards the end of the day, after prolonged standing or walking long distances. A night's rest relieves the condition. Joint pain during pregnancy is caused by the following reasons:
- Lack of vitamins and minerals. The biggest role is the deficiency of calcium and vitamin D, which leads to osteomalacia. A characteristic of the manifestation of the symptom is a feeling of pain not only in the joints, but also in the bones, fatigue, the presence of other signs of hypocalcemia and hypovitaminosis D - caries, brittle nails, muscle weakness, muscle pain and frequent occurrence of ARVI.
- Significant weight gain. Joint discomfort is more often a problem for pregnant women who gain a lot of weight or who are obese. The pains at the end and finally in the middle of the day are felt in the hip joints, knees, ankles, whose cartilages experience loads several times higher than permissible. To alleviate the condition, women consciously limit physical activity, which leads to even faster weight gain.
- Softening of cartilage and ligaments. About half of pregnant women experience pelvic joint discomfort caused by the action of the hormone relaxin. In most cases, the discomfort has the character of pain in the pubic area and hip joints. In a pathological course with the development of symphysitis, painful sensations are replaced by pain that intensifies when pressing the uterus, trying to separate the legs, during sex. The appearance of pain in the pubic area is a serious reason for visiting an obstetrician-gynecologist.
- Carpal tunnel syndrome. A specific manifestation that occurs during the 2-3 trimester in almost 20% of pregnant women is the so-called tunnel syndrome. The cause of the disorder is swelling of the soft tissues of the hands and compression in the carpal tunnel of the nerves that pass to the fingers. In addition to pain in the small joints of the hand, patients complain of tingling of the skin, numbness and a crawling sensation. The condition improves with the raised position of the arms.
obesity
In people who are overweight, the pressure on the cartilage tissue increases, which leads to its faster wear. The degenerative-dystrophic process usually affects the large joints of the lower limbs and intervertebral joints. The disorder increases as obesity progresses. Discomfort in the joints first manifests itself in the form of pain without temperature until the end of the day, after which the increasing destruction of cartilage leads to the development of deforming arthrosis, spondylosis, osteochondrosis with an acute pain syndrome that limits the patient's motor activity.
Acute infections
Body and joint pains are one of the early (prodromal) signs of very acute respiratory viral infections. The main causes of discomfort in the joints are intoxication of the body due to the spread of viruses and bacteria, the accumulation of toxins and the development of an inflammatory process. Usually, the patient complains that the whole body hurts, mild and moderate pain is noted both in the joints and in the muscles and bones. The symptom is accompanied by weakness, fatigue, insomnia and frequent awakenings. Simultaneously with signs of pain and general malaise, chills and hyperthermia are observed.
Joint and body pains are most pronounced during flu. Up to 50% of patients experience constant pain in the legs, arms and torso. The intensity of the pain is so high that it becomes difficult for a person to perform the simplest actions - get out of bed, go to another room, get a glass of water. The situation is aggravated by a high (febrile) temperature and a severe headache. A sore throat and stuffy nose appear after a few hours or even days. Less joint discomfort occurs with parainfluenza, an adenovirus infection.
A feeling of pain in the joints is possible with acute infectious lesions of the gastrointestinal tract - food toxic infections, salmonellosis. Joint pains of varying intensity appear suddenly a few hours after consuming contaminated food and are combined with a sharp increase in temperature, severe chills and headache. Pain is preceded by nausea, vomiting, pain in the abdominal cavity, foul-smelling diarrhea with mucous and sometimes bloody impurities.
Collagenoses
Joint pain is a harbinger of most diseases occurring with autoimmune inflammation of connective tissue, including joint tissue. Localization, distribution and intensity of unpleasant sensations are determined by the characteristics of a particular collagenosis. The general patterns are the participation of certain groups of joints in the process, a gradual increase in sensations to excruciating debilitating pain, observed first during movements, and then at rest. Deformation of the joints is possible. The main systemic inflammatory causes of the disease:
- rheumatism. The symptom is "constant": pains and then pain are felt in turn in the large joints of the arms and legs - elbows, shoulders, hips, knees, ankles. The affected areas are swollen. Joint discomfort is often preceded by a sore throat. With treatment, the changes in the joints are reversible.
- Rheumatoid arthritis. Unpleasant sensations often appear after 40 years. A typical feeling of pain in the small joints of the hands and feet, combined with noticeable swelling and morning stiffness of movements. In the future, pain and distortion of the joints come to the fore.
- Systemic scleroderma. It is characterized by variable localization of pain sensations, the presence of stiffness in the morning in the joints of the hands, elbows and knees. The pains are usually symmetrical. The swelling is short-lived. Due to skin sclerosis, the mobility of the joints is limited, damage to the tendons causes a feeling of friction when moving.
Osteoarthritis
The pain syndrome in the initial stages of the disease is mild and is perceived as discomfort, pain in the joints of the legs and, less often, the hands. The immediate cause of osteoarthritis is degeneration and destruction of cartilage tissue. Usually, pulling or painful sensations without fever appear in adulthood and old age. The pain may start earlier in the presence of occupational hazards (vibrations, heavy physical work). Gradually the joints stiffen, the person experiences severe pain and difficulty walking and taking care of himself.
Metabolic disorders
The causes of metabolic disorders in which joint pain occurs are insufficient supply of vitamins, minerals, accelerated accumulation or excessive excretion of metabolic products. Unpleasant sensations are caused by inflammatory or dystrophic processes, have different severity and most often serve as a manifestation of pathological conditions such as:
- osteoporosis. When calcium is washed out of the bone tissue, the articular surfaces of the bones become brittle, the cartilage thins, which is accompanied by painful sensations. The pain syndrome increases gradually from mild pain to severe arthralgia, combined with unpleasant sensations in the bones and muscle weakness. The joints that experience the maximum load are most often affected - hip and knee, less often the shoulder, elbow and ankle.
- gout. Mild pain in the big toe is already a problem in the preclinical stages of the gouty process. There may be pain in the knees, elbows, wrists and fingers. The accumulation of urates in the joint cavity leads to a rapid manifestation of the disease with a change from pain to acute painful joint pain that does not subside for several hours. The affected joint is hot to the touch. There is redness of the skin and limited movements.
Oncological diseases
In acute and chronic leukemia, widespread bone-joint pains often appear, followed by pain, even before noticeable pathological changes in the general blood test and other clinical symptoms - general malaise, night sweats, fever, loss of appetite, bleeding. Unpleasant sensations are at first periodically painful, then constantly strong, exhausting the patient.
Hodgkin's lymphoma and lymphogranulomatosis are characterized by a combination of joint pain with muscle discomfort, weakness, enlarged lymph nodes and other lymphoid formations. Pain sensations are frequent, usually moderate. With osteosarcomas, there is a short-term pain in the knee joint and thigh muscles, which increases at night and with exertion turns into constantly increasing pain with limping. Other joints are less often affected by this pathology.
Joint injuries
Joint pain is provoked by mild traumatic injuries that cause damage to the ligaments around the joint and bruising of the soft tissues of the joint area. Stronger pain occurs with damage to the meniscus. The symptom is clearly related in time to a blow, fall or awkward movement. Discomfort is usually felt in one affected joint, less often it spreads to neighboring parts of the body.
Chronic infectious processes
Possible reasons for a feeling of pain in the joints, which occurs without a fever or against the background of a low-grade fever, are long-lasting infections. In patients suffering from chronic infectious and inflammatory diseases, discomfort in the joints is a consequence of intoxication of the body or direct damage to the joint tissues by microorganisms (usually streptococci, mycoplasma, chlamydia). The appearance or intensification of pain may indicate exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis, sinusitis, genitourinary infections, adnexitis, pyelonephritis.
Distinctive features of joint pain in general chronic infections occurring with intoxication are moderate severity of joint discomfort, gradual development, periodic strengthening and weakening of symptoms. In patients suffering from tuberculosis and hematogenous osteomyelitis, the background for the development of painful painful sensations is an increase in temperature to subfebrile levels, general malaise - fatigue, weakness, weakness. Without treatment, the patient's condition progressively worsens.
Complications of pharmacotherapy
Taking some medications can be complicated by pain and moderate pain in the small joints of the hands. The unpleasant sensations are not accompanied by redness or deformation of the joints. Patients may complain of muscle pain, fever, skin rashes and other manifestations of drug allergies. Discomfort quickly disappears after stopping the drug that provoked it, and it is less likely that special treatment will be required for complications that have arisen. Pain and mild arthralgia are caused by:
- antibiotics: penicillins, fluoroquinolones.
- Sedatives: phenazepam, diazepam, lorazepam, etc.
- contraceptives: combined oral contraceptives (COCs).
Rare reasons
- Inflammation of the respiratory system: pneumonia, bronchitis, tracheitis.
- Intestinal pathology: non-specific ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease.
- Skin diseases: psoriasis.
- Endocrine disorders: diabetes mellitus, diffuse toxic goiter, hypothyroidism, Itsenko-Cushing's disease.
- Autoimmune processes: Hashimoto's thyroiditis, vasculitis.
- Fascial injury: necrotizing fasciitis in convalescent stage.
- Congenital defects of bones and joints.
Research
To determine why joint and bone pain is felt, it is necessary to consult a therapist or family doctor who will conduct an initial diagnosis and prescribe examinations by specialized specialists. Taking into account the nature of the unpleasant sensations, the speed of their occurrence and accompanying symptoms, in order to determine the cause of the disorder, the following is recommended:
- Laboratory blood test. An assessment of the leukocyte count and the ESR level is necessary to rule out infections, inflammation and oncohematological processes. In systemic diseases, it is important to measure the content of total protein, the ratio of protein fractions in the blood, specific proteins in the acute phase, markers of rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammations. Tests for the concentration of vitamins, electrolytes (especially calcium), and uric acid help diagnose metabolic disorders.
- Bacteriological examination. A bacterial culture is needed if there is a possibility that the pain in the joints and the whole body is infectious. Urine, feces, sputum and discharge from the urogenital tract are collected for examination. To select a regimen of antimicrobial therapy, sensitivity to antibiotics is determined. In doubtful cases, microscopy and culture are supplemented with serological reactions (RIF, ELISA, PCR).
- Ultrasound of joints. It is usually used for clear localization of painful sensations and suspicion of the presence of rheumatic diseases. Ultrasound of the joint allows us to study its structure, identify the destruction of cartilage and bone, preclinical inflammatory changes and examine the condition of the periarticular soft tissues. The advantages of the method are accessibility, non-invasiveness and high informativeness.
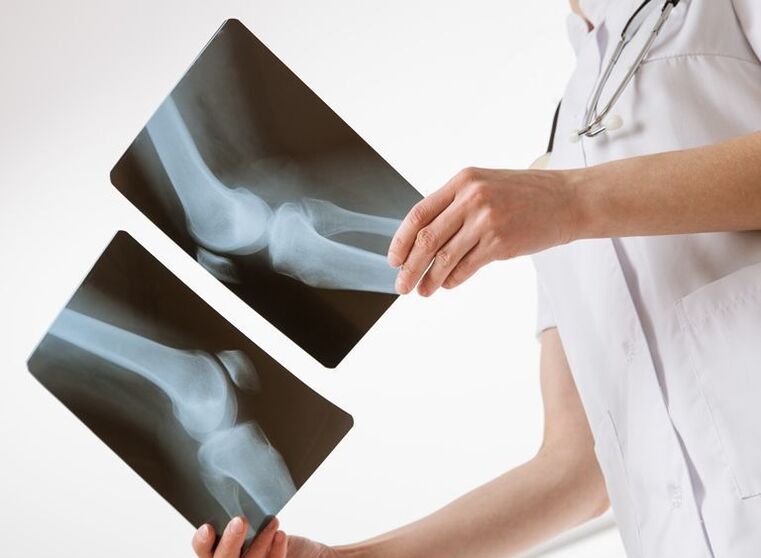
- X-ray techniques. X-rays of the joints reveal changes in the width of the joint space, hardening of the soft tissues, the presence of calcifications, osteophytes and erosions of the joint surfaces. To improve diagnostic efficiency, special techniques are used - contrast arthrography, pneumoarthrography. In the initial stages of the lesion, tomography (MRI, CT of the joints) is considered more indicative. Bone density can be conveniently assessed using densitometry.
- Invasive research techniques. In some cases, to determine the cause of pain in the joints, a puncture is performed with a biopsy of the cartilage, the inner lining of the synovial membrane and the tophi. The morphological analysis of the biopsy and the examination of the synovial fluid reflect the nature of the pathological processes occurring in the joints. Simultaneous collection of materials with visual examination of the joint cavity is convenient to perform during arthroscopy with tissue biopsy.
A less common way to diagnose the cause of joint pain is scintigraphy with the introduction of technetium, which accumulates in the affected tissues. In recent years, there has been a growing interest in joint thermography as a modern non-invasive method for detecting inflammatory diseases, tumors and blood circulation disorders in joints and peri-articular tissues. If the number of formed elements in the clinical blood test decreases, an extra-articular bone puncture is performed. Patients with joint pain without fever are recommended to consult a rheumatologist and orthopedic traumatologist.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
For joint pains associated with physical exertion, no special treatment is required, a long rest with dosing of the load is sufficient. Unpleasant joint sensations that occur during pregnancy usually disappear on their own after pregnancy or are corrected by controlling weight and taking vitamin and mineral supplements. Elderly patients and obese patients are advised to change their lifestyle: adequate physical activity, a diet with an appropriate calorie content with a sufficient content of plant foods.
Pain in the bones, joints and muscles, combined with general malaise and fever, increased pain and pulling sensations up to severe pain and the development of constant pain are an indication for consulting a doctor. To reduce joint discomfort caused by ARVI, it is recommended to rest, drink enough water, rosehip infusions and dried fruits. As long as serious diseases that provoke pain in the joints are not excluded, self-medication with painkillers, long-term unsuccessful application of compresses, lotions, potions, etc. are unacceptable.
Conservative therapy
You can get rid of joint pain with the right treatment aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease and individual units of the mechanism of its development. Etiopathogenetic therapy is usually supplemented by symptomatic drugs that quickly reduce the severity of unpleasant and painful pain. The treatment regimen for diseases occurring with joint pain may include:
- Antimicrobial agents. The main therapy of infections is based on the prescription of antibiotics to which the pathogen is sensitive. In severe cases, broad-spectrum drugs are used until the sensitivity of the microorganism is established.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They reduce the production of inflammatory mediators and thus inhibit inflammatory processes in the joints. Acting on the central pain receptors, they reduce the degree of joint discomfort. It is used in the form of tablets, ointments, gels.
- Corticosteroids. They have a strong anti-inflammatory effect. Hormonal therapy is the basis of the treatment of systemic collagenoses. In severe and resistant forms of the disease, corticosteroid drugs are combined with immunosuppressants to enhance the effect.
- Chondroprotectors. They act as a substrate for the synthesis of protein glycans, a sufficient amount of which increases the elasticity of articular cartilage. Nourishes cartilage tissue and restores its damaged structure. Intra-articular administration of drugs is possible.
- Xanthine oxidase inhibitors. It is used as an anti-gout medicine. They block the key enzyme required for the synthesis of uric acid, thereby reducing its concentration in the body and promoting the dissolution of existing urate deposits.
- Vitamin-mineral complexes. It is recommended for the treatment of joint pain caused by metabolic disorders. The most commonly used preparations contain calcium and vitamin D. They are also an element of complex therapy for inflammatory and metabolic diseases.
- Chemotherapeutic agents. They serve as the basis for most treatment regimens for various types of oncohematological pathologies. Depending on the clinical variant and the severity of the neoprocess, they are combined with radiation therapy and surgical interventions.
Physiotherapy
After establishing the exact cause of the pain and subsiding of the acute inflammation, the patients, with the exception of cancer patients, are prescribed physiotherapy and remedial exercise. Microwave and ultrasound therapy, electrophoresis and pulse currents have a good anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect. In case of chronic pathology, physiotherapy treatment is carried out for several months and is supplemented by spa therapy.
































